When managing finances, it’s essential to understand the various documents provided by banks, as they serve distinct purposes. Two commonly confused documents are bank statements and bank certificates. While banks issue both, they are used for different reasons and contain different types of information.
Bank Statements are essential for tracking financial activity, identifying discrepancies, and providing proof of income or expenses. They are often required for loan applications, mortgage approvals, or tax audits. On the other hand, bank Certificates are used to verify specific account details or financial standing. They are commonly needed for visa applications, job verifications, or legal proceedings.
This article will demonstrate how Bank Statements and Bank Certificates are different from each other in terms of use, purpose, accessibility, legal weight, etc.
Bank Certificate vs Bank Statement – Key Differences
To help you understand their differences clearly, we’ve created a concise comparison table below.
| Comparison | Bank Certificate | Bank Statement |
|---|---|---|
| Format | A concise, formal document issued on bank letterhead, often signed and stamped. | A detailed, multi-page document listing all transactions over a specific period. |
| Information shared | Confirms specific details like account holder name, account status, balance, etc. | Provides a comprehensive record of all transactions, balances, fees, and interest. |
| Validity | Valid as of the date of issuance; may have a short validity period (e.g., 3 months). | Reflects historical data; validity depends on the purpose (e.g., 3-6 months old). |
| Frequency of issuing | Issued only upon request by the account holder. | Typically issued monthly, but can be requested for specific periods. |
| Legal weight | Official proof of account details or financial standing; often required for legal, immigration, or employment purposes. | Used as evidence of financial activity; often required for loans, taxes, or audits. |
| Used for | Visa applications, proof of funds, job verifications, and legal compliance. | Budgeting, financial tracking, loan applications, tax filings, or audits. |
| Accessibility | It requires a formal request from the bank; it may take a few days to process. | Easily accessible via online banking, email, or physical copies from the bank. |
What Is a Bank Certificate?
A bank certificate is an official document issued by a bank to verify specific account details, such as account ownership, current balance, or account status. It serves as formal proof for legal, immigration, or financial requirements like visa applications, loans, or compliance checks.
Common Types Of Bank Certificates
Banks issue several types of certificates, including:
- Balance Certificate: Confirms the current account balance.
- Account Confirmation Letter: It verifies account ownership, type, and opening date.
- Creditworthiness Certificate: It shows the credit history and repayment capacity.
- Fixed Deposit (FD) Certificate: Provides FD terms, maturity date, and interest.
- Solvency Certificate: Validates financial stability for large transactions or visas. These certificates are often required for visa applications, loan approvals, legal disputes, or employment background checks.
Key Features Of Bank Certificates
Here are some key features of bank certificates:
- Contains: Account holder’s name, account number, balance (as of issuance date), account status (active/inactive), and bank seal/signature.
- Validity: Typically valid for 3–6 months, depending on the institution’s policy.
- Usage: Used for legal compliance, visa processes, proof of funds, or employment verification.
- Formality: Requires a formal request to the bank; not automatically generated.
What Is A Bank Statement?
A bank statement is a periodic summary of transactions for a bank account over a specific period (usually monthly). It details deposits, withdrawals, transfers, fees, interest earned, and balances, providing a comprehensive record of account activity.
Banks issue statements to help customers track finances, verify income/expenses, and resolve discrepancies. They are often used for budgeting, loan applications, tax filing, or audits.
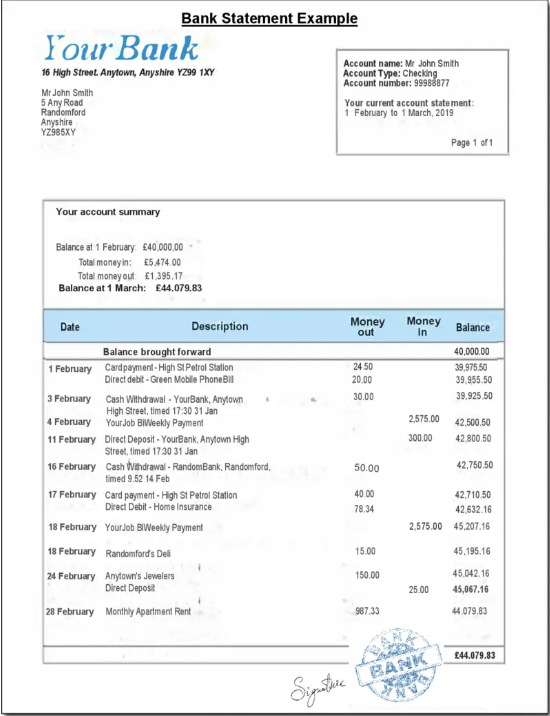
Types Of Bank Statements
Mentioned below are the types of bank statements:
- Paper Statements: Mailed physically; these include transaction lists, account summaries, and bank notices.
- Electronic Statements (e-Statements): Digital versions accessible via online banking or email, often downloadable as PDFs.
- Business Statements: Tailored for business accounts, these may include bulk transactions, payroll details, and multi-account summaries.
- Credit Card Statements: Focus on credit transactions, payments, due dates, and rewards (if applicable).
- Mini Statements: Short-term summaries from ATMs or apps showing recent transactions (e.g., last 10 entries).
Key Features Of A Bank Statement
Here are the key features of bank statement:
- Transaction Details: Dates, amounts, and descriptions of deposits, withdrawals, and transfers.
- Account Summary: Opening/closing balances, interest earned, and fees charged.
- Period Covered: Clearly states the beginning and end dates of the statement cycle.
- Account Information: Shows the account holder’s name, number, and branch details.
- Proof of Activity: It is used to verify income, address, or financial behavior for loans, visas, or rentals.
- Digital Accessibility: Often available instantly via online banking or mobile apps.
Critical Differences Between A Bank Statement And A Bank Certificate
Here’s a detailed comparison between bank statements and bank certificates, highlighting lesser-known facts and contextual insights to help users make informed decisions.
1. Purpose
Here, we will differentiate between bank certificates and bank statements on the basis of their purpose.
Bank Certificate
A bank certificate acts as a snapshot of static account data at a specific moment. It’s used for formal validations where proof of financial standing is critical—think embassy visa interviews, court affidavits, or corporate tenders. For example, some countries demand a solvency certificate with a minimum validity window (e.g., 30 days) for visa approvals.
Bank Statement
A bank statement is a dynamic financial diary tracking inflows, outflows, and behavioral patterns over weeks or months. Beyond personal budgeting, it’s used by landlords to assess rental reliability or by immigration officers to detect suspicious transaction patterns (e.g., sudden large deposits).
2. Format
The term “format” refers to the structure or layout in which the information is presented within these documents. Each document must adhere to specific standards to ensure it is clear, easy to understand, and legally acceptable. Mentioned below is the difference between bank certificates and bank statements on the basis of their format.
Bank Certificate
- Often includes anti-fraud features: holographic seals, QR codes for online verification, or unique serial numbers.
- Some banks issue bilingual certificates (e.g., English + local language) for international use.
- No transaction history—focuses solely on account metadata (e.g., “active since 2015” or “balance as of 10th Jan”).

Bank Statement
- Customizable periods: While monthly is standard, users can request “rolling statements” (e.g., last 45 days) for flexible needs.
- Business statements may include merchant IDs, VAT details, or client references for accounting reconciliation.
- Digital statements often allow interactive filtering (e.g., sorting by transaction type).
3. Issuance
Depicted below are the differences between bank certificates and bank statements on the basis of their issuance
Bank Certificate
- Not all certificates are equal: A “balance certificate” might be instantly generated via mobile apps in some banks (e.g., Singapore’s DBS), while a “solvency certificate” may require branch visits and manager approval.
- Regional quirks: In India, certificates often need a “wet ink” signature for government submissions, whereas EU banks may accept e-signatures.
Bank Statement
- Instant vs. delayed access: E-statements are downloadable immediately, but certified/notarized statements (for legal use) can take days.
- Archival limits: Some banks purge statements older than 7 years, requiring advance requests for historical data.
4. Legal Weight
the term “legal weight” typically refers to the authenticity and official validity of the documents provided by the bank. These documents are legally recognized as valid records of a person’s or a business’s financial status, transactions, or financial history. Here are the differences between bank certificates and bank statements in terms of legal weight.
Bank Certificate
- Irreplaceable in specific scenarios: For example, Japanese visas often reject statements and strictly require a balance certificate.
- Fraud risks: Certificates are prone to forgery due to their simplicity, so institutions increasingly use QR-linked digital certificates (e.g., UAE’s Emirates NBD).
Bank Statement
- Contextual credibility: While accepted for loans, statements may require supplementary proof (e.g., salary slips) if transactions lack descriptors.
- International hurdles: Older paper statements might need apostille certification for cross-border use (e.g., EU property purchases).
How To Obtain Bank Certificates?
To obtain bank certificates, follow the mentioned steps:
- Visit Your Bank Branch: Bring valid ID (e.g., passport, driver’s license) and account details.
- Request a Bank Certificate: Specify the purpose (e.g., visa application, loan) and required details (e.g., current balance).
- Wait for Processing: Some banks issue it instantly; others may take 1–3 business days.
- Collect the Document: Receive a stamped/sealed certificate either in person or via email.
Alternative: Use online banking/mobile apps (if available) to request and download a digital copy.
How To Obtain Bank Statements?
Mentioned below is a step-by-step guide by which a user can obtain bank statements:
1. Online Banking
- Log in to your account.
- Navigate to “Statements” or “Transaction History.”
- Select the date range and download/email the PDF.
2. Mobile App
Open your bank’s app, go to “Statements,” and generate/view the document.
3. ATM
Insert your card, and select “Print Statement” (limited to recent transactions).
4. Branch Visit
Request a printed statement at the counter (may incur a fee).
5. Customer Service
Call your bank to mail/email statements to your registered address.
Conclusion: “Bank Certificate vs. Bank Statement: Instant Proof And Full Transaction History”
Understanding the distinctions between bank certificates vs. bank statements is crucial for effective financial management. While a bank certificate serves as a formal document to validate account-specific details like ownership, balance, or account status, a bank statement provides a comprehensive record of financial activity over a specific period.
Each document serves distinct purposes: bank certificates are indispensable for legal, immigration, or formal verification needs, whereas bank statements are vital for tracking financial health, budgeting, or applying for loans. By knowing their differences, formats, issuance processes, and legal implications, you can ensure you request the right document for your specific needs, saving time and avoiding potential misunderstandings.

Anshu is a content enthusiast with a passion for exploring entertainment and media trends. At YouTrial.TV, he brings his knowledge of streaming platforms and recommendations to help users make the most of their viewing experience. Anshu enjoys staying up-to-date with the latest in the digital world and sharing valuable insights with readers.